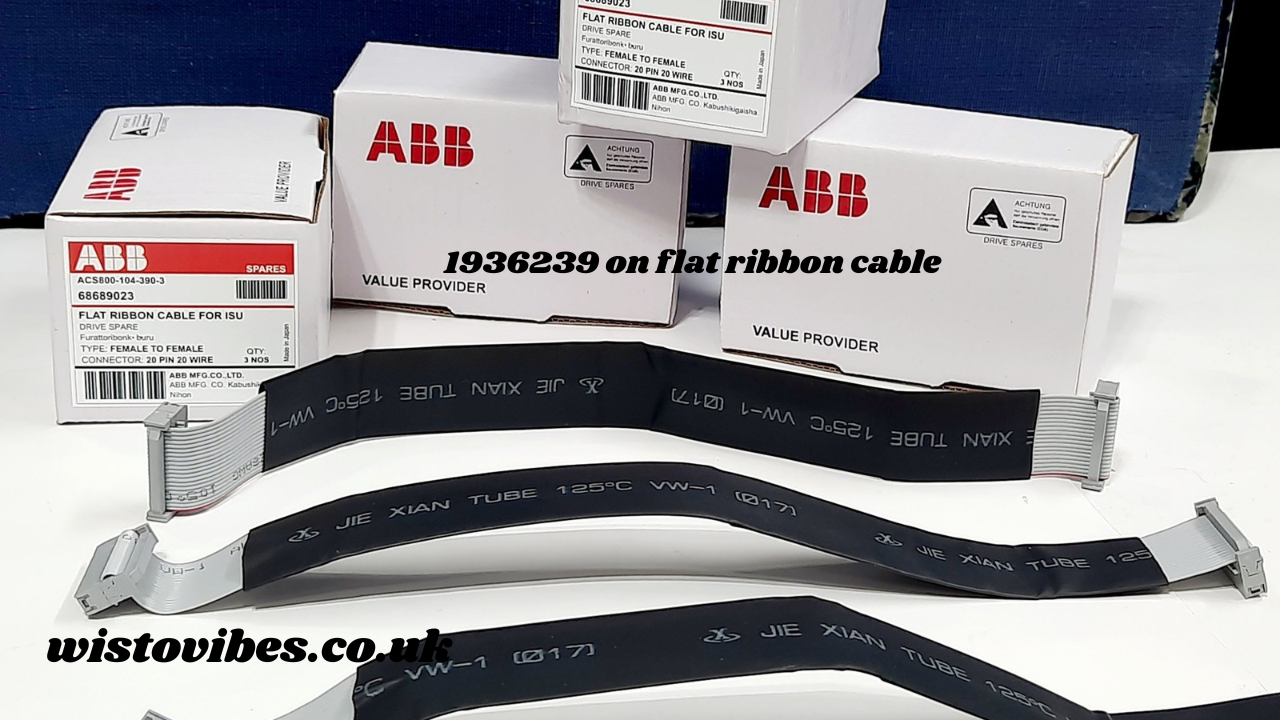
Introduction to 1936239 on Flat Ribbon Cable
The term “1936239 on flat ribbon cable” may seem highly technical, but it carries significant importance in electronics manufacturing, prototyping, and repair industries. This term refers to a specific part number, 1936239, typically associated with connectors or interfaces used on flat ribbon cables within electronic assemblies, servers, robotics, and industrial automation.
Flat ribbon cables are widely used due to their compact profile, flexibility, and ability to carry multiple conductors simultaneously in a flat, organized manner, reducing clutter in control panels and inside electronic devices. The 1936239 component on flat ribbon cable provides stable connectivity, efficient signal transmission, and secure mechanical interfaces, making it valuable in modern electronics.
This article will help you understand “1936239 on flat ribbon cable” in detail, exploring its uses, design considerations, technical specifications, and why it matters in industrial and consumer applications.
What is a Flat Ribbon Cable?
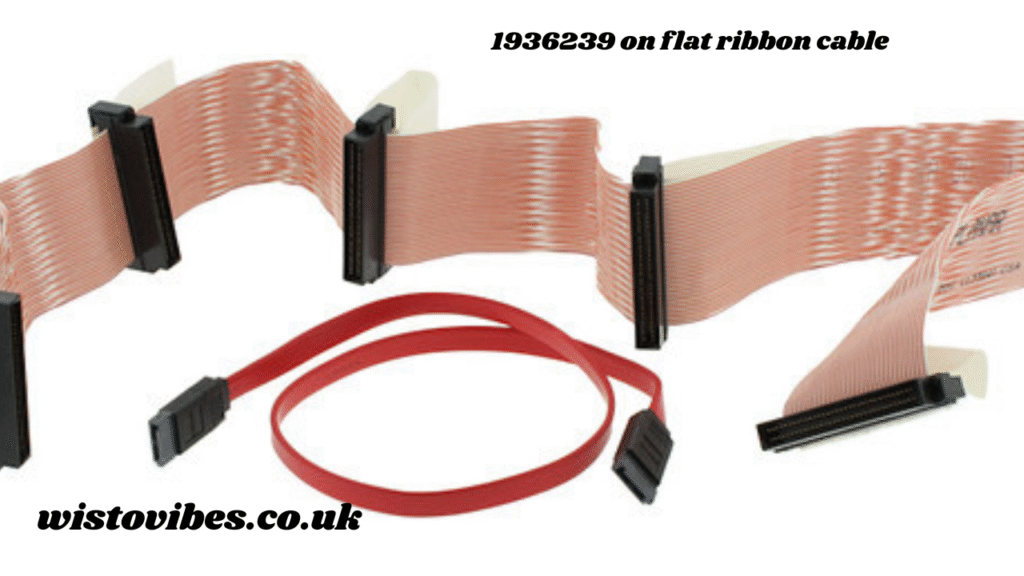
A flat ribbon cable is a type of electrical cable that consists of multiple insulated wires arranged parallel to each other in a flat, wide strip. They are commonly used in:
- Computers: for internal connections like hard drives, optical drives, and floppy disk drives.
- Printers and Scanners: for precise signal transmission.
- Industrial Machines: connecting sensors, controllers, and displays in tight spaces.
- Consumer Electronics: where compact, organized cabling is essential.
The design of flat ribbon cables allows for easy mass termination, using connectors such as the 1936239 part, to simplify wiring and ensure efficient signal integrity across all connected conductors.
Understanding 1936239 on Flat Ribbon Cable
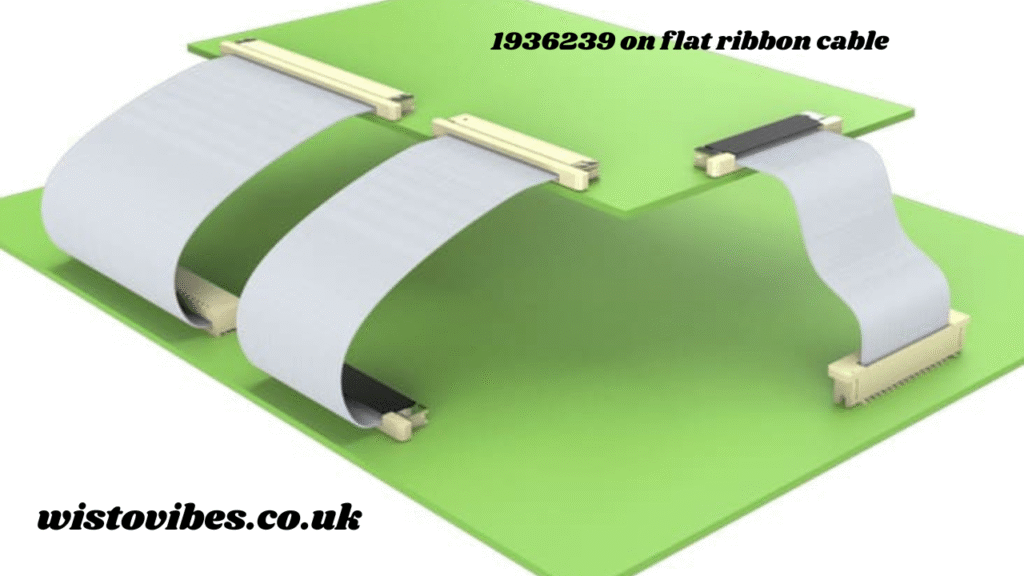
When you encounter the term “1936239 on flat ribbon cable”, it typically refers to a specific connector part number (1936239) used with flat ribbon cables for structured, stable connections.
The 1936239 component is designed to:
- Align precisely with the flat conductors of the ribbon cable.
- Allow secure latching and locking to maintain mechanical stability.
- Support signal integrity by ensuring clean electrical contact across each conductor.
- Enable quick connections and disconnections during prototyping or maintenance.
This part may belong to a series of IDC (Insulation Displacement Contact) connectors or similar connector types, which allow technicians and engineers to terminate the cable quickly without soldering, reducing time and improving consistency in assembly lines.
Why 1936239 Matters in Electronics
Using “1936239 on flat ribbon cable” provides clear advantages, including:
- Space Efficiency: The flat structure and low profile of the connector suit compact control panels and devices.
- Ease of Installation: IDC or similar connectors like 1936239 allow for easy assembly, saving time in production.
- Reliability: It offers stable connections in environments with vibrations or movements, crucial for industrial machinery.
- Signal Integrity: By maintaining consistent contact across all pins, it helps reduce crosstalk and maintains the quality of transmitted signals.
Whether in data acquisition systems, CNC machinery, robotics, or server environments, 1936239 on flat ribbon cable becomes a backbone for interconnectivity.
Technical Specifications to Consider
While exact specifications depend on the manufacturer, common features of 1936239 on flat ribbon cable may include:
- Pitch: (distance between each conductor pin) often 1.27 mm (0.05 inches) for standard ribbon cables.
- Pin Count: varying from 10, 14, 16, 20, up to 64 or more depending on the cable and the connector application.
- Current Rating: typically around 1–2A per contact, depending on conductor size and cable length.
- Voltage Rating: usually up to 300V depending on insulation type.
- Operating Temperature: ranges from -40°C to +105°C.
- Material: housing often made from high-quality plastic or thermoplastic with tin- or gold-plated contacts for corrosion resistance.
Understanding these specifications ensures you select 1936239 on flat ribbon cable appropriately for your project’s voltage, current, and environmental conditions.
Application Scenarios of 1936239 on Flat Ribbon Cable
1. Industrial Automation:
In programmable logic controllers (PLCs), sensors, and human-machine interfaces, 1936239 on flat ribbon cable connects different modules while reducing wiring complexity.
2. Computer and Server Assemblies:
Flat ribbon cables with 1936239 connectors are used to connect drives, control boards, and expansion cards within computer cases and server racks.
3. Robotics:
Robotic arms and automated guided vehicles (AGVs) utilize these cables for signal and power routing in restricted spaces.
4. Consumer Electronics:
Devices like printers, scanners, and even some audio equipment utilize 1936239 on flat ribbon cable for reliable internal connections between control boards and mechanical components.
Best Practices When Using 1936239 on Flat Ribbon Cable
To maximize the benefits of 1936239 on flat ribbon cable, consider the following:
- Cable Orientation: Align the polarity stripe of the ribbon cable with pin 1 of the connector to avoid miswiring.
- Strain Relief: Use appropriate strain relief methods to prevent mechanical stress on the connector.
- Proper Crimping: Utilize certified IDC tools if applicable to ensure consistent and clean terminations.
- Environmental Considerations: If used in harsh environments, consider additional protective enclosures or sealed variants of the 1936239 connector.
- Regular Inspection: Periodically check for wear, corrosion, or loose connections, especially in industrial applications with vibration.
Common Challenges with 1936239 on Flat Ribbon Cable
While using 1936239 on flat ribbon cable is efficient, challenges can arise:
- Mismatched Pinout: Careful attention to pin mapping is essential to avoid electrical failures.
- Cable Damage: Bending flat ribbon cables beyond their designed flexibility can damage internal conductors.
- Connector Wear: Repeated plugging and unplugging may wear out contact surfaces over time.
- Electromagnetic Interference (EMI): Long ribbon cables without shielding can pick up noise, so consider cable length and routing carefully.
Addressing these challenges with proper handling and design planning ensures the longevity and reliability of your electronic assemblies using 1936239 on flat ribbon cable.
The Future of 1936239 on Flat Ribbon Cable in Electronics
Despite advances in flexible printed circuit boards (FPCBs) and micro-coaxial cables, flat ribbon cables with 1936239 connectors remain relevant due to their cost-effectiveness, ease of termination, and availability in various configurations.
In prototyping labs and small-scale production, 1936239 on flat ribbon cable continues to offer quick, reliable connectivity for engineers developing new hardware products and testing environments.
Moreover, as IoT and robotics expand, structured cabling using 1936239 will remain integral to cost-effective signal and power distribution within compact enclosures.
Conclusion
“1936239 on flat ribbon cable” is more than just a part number—it represents a reliable, efficient way to handle connectivity in electronics. By understanding what 1936239 represents, its technical features, application areas, and handling practices, engineers, technicians, and hobbyists can effectively integrate it into their designs.
The widespread use of flat ribbon cables paired with connectors like 1936239 ensures organized wiring, space savings, and stability in applications ranging from industrial machinery to personal computing. As technology evolves, this trusted method of connectivity remains a fundamental building block in maintaining clean, reliable, and organized wiring structures in electronic assemblies.
Also Read : Brian Harmon UX Designer, User-Centered Visionary, Career, Approach, Projects, and More?




